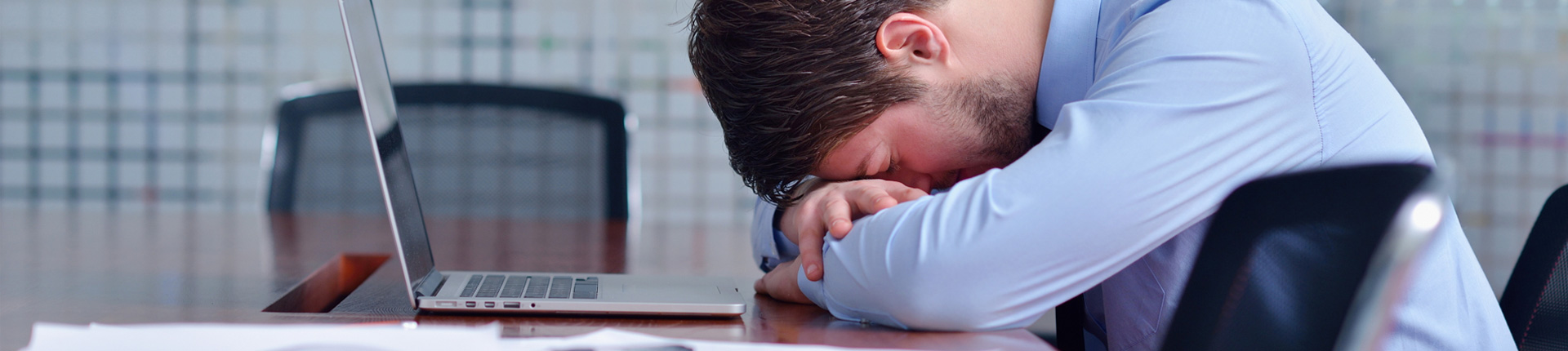

Brain aneurysm
- Home
- Brain aneurysm
Brain aneurysm is an abnormal bulge in the brain’s blood vessel. When it leaks or ruptures, it causes bleeding into the brain, otherwise known as hemorrhagic stroke. A type of hemorrhagic stroke called subarachnoid hemorrhage occurs in the space in between the brain and the tissues covering it. This is the type of ruptured aneurysm that requires emergency treatment as it is life threatening.
A ruptured aneurysm always exhibits the following common symptoms:
Leaking Brain Aneurysm
A small amount of blood can leak as a result of aneurysm leak. Severe headache that is sudden can only be caused by the leaking (sentinel blood).A leaking is always followed by a more serious rupture.
Un-Ruptured Brain Aneurysm
If the un-ruptured aneurysm is small it may not cause any symptoms at all. Nerves and tissues on the brain can be pressed by un-ruptured aneurysm that is large and it causes:
There are many conditions and factors that can lead to the formation of brain aneurysms.
The most common are smoking and uncontrolled high blood pressure. There are also genetic conditions including connective tissue disorders and polycystic kidney disease that can lead to aneurysm formation.
The majority of brain aneurysms never cause health problems; because of that, many go undiagnosed. Brain aneurysms typically are discovered only after a rupture, when the unruptured aneurysm is causing head pain, or when someone is undergoing tests for another condition. There are four main tests that can detect a brain aneurysm.
The two common treatment methods for ruptured brain aneurysm are surgical clipping and endovascular coiling.
Surgical clipping involves a procedure of closing off an aneurysm. The doctor places a metal clip on the blood vessel that feeds the aneurysm to stop blood from flowing through it.
Endovascular coiling is less invasive. A surgeon inserts a catheter into the artery from the groin. Through this catheter, a wire is inserted to coil up inside the aneurysm to disrupt the blood flow.
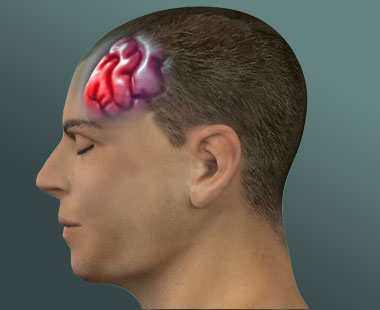
What is head injury?A traumatic brain injury, also referred to an acquired brain injury, occurs when someone suffers a sudden…
read more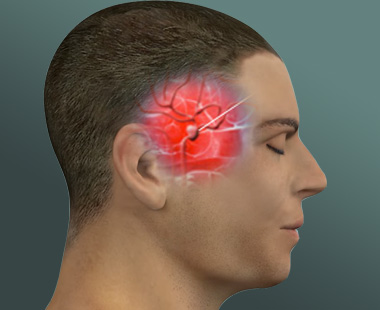
What is Brain Aneurysm?Brain aneurysm is an abnormal bulge in the brain's blood vessel. When it leaks or ruptures, it…
read more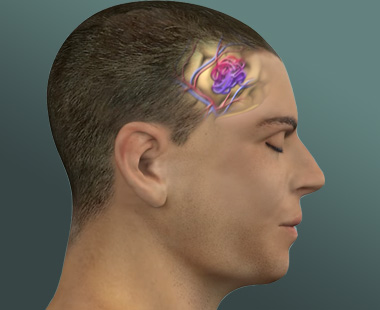
What is a brain arteriovenous malformation ?Normally, arteries carry blood containing oxygen from the heart to the brain, and veins…
read more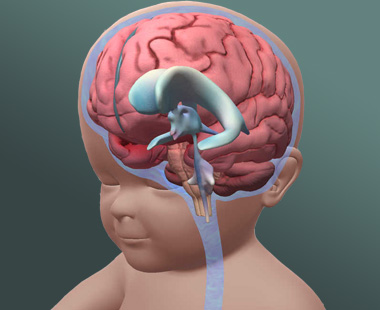
What is Hydrocephalus?Hydrocephalus is commonly referred to as "water on the brain." The so-called "water" is actually cerebrospinal fluid (CSF),…
read more